It is understood that the Xiangjing High-Speed Railway began construction in September 2022. The full-line track laying was successfully completed in April 2025, and joint debugging and testing started in June 2025. During the joint debugging and testing phase, the railway department tested 12 major items, including tracks, bridges, traction power supply, communication, signaling, and customer service systems. A total of 1,759 inspection trains were operated, covering a detection distance of 43,300 kilometers. This comprehensively inspected and verified the functions of various fixed facilities and mobile equipment, with technical performance meeting national and industry technical standards and satisfying the conditions for opening and operation.
During the operational testing, the principle of “safety, efficiency, and order” was followed, with the overall goal of “achieving the design speed value in one go” to ensure that pre-opening preparations are in place, laying a solid foundation for the opening and operation of the Xiangjing High-Speed Railway. This also means that after the Xiangjing High-Speed Railway is put into operation, the maximum operating speed will reach 350 kilometers per hour.
The test train departs from Xiangyang East Station.
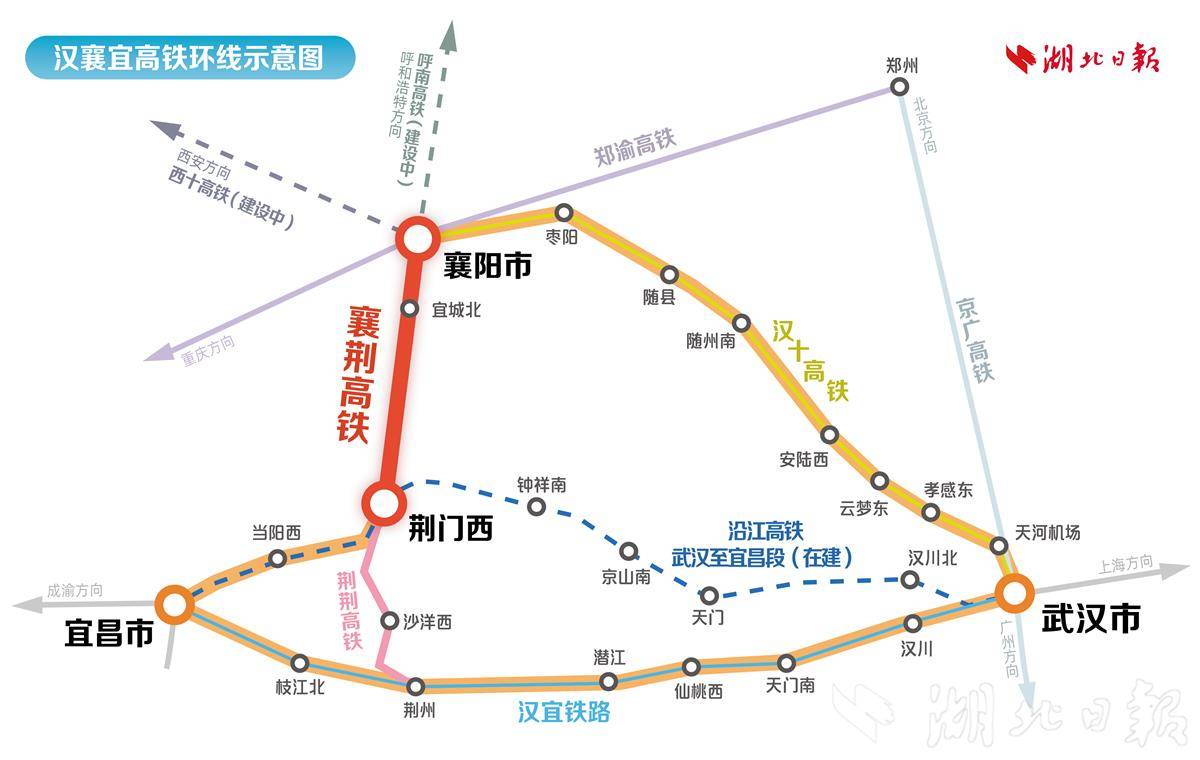
The Xiangjing High-Speed Railway connects to the Zhengzhou-Chongqing High-Speed Railway in the north and the Shanghai-Chongqing-Chengdu High-Speed Railway in the south. It is an important part of China’s “Eight Vertical and Eight Horizontal” high-speed rail network, specifically the Hohhot-Nanning Corridor. After the Xiangjing High-Speed Railway is completed and opened, the high-speed rail journey from Xiangyang to Jingmen will take only about 30 minutes. It will form Hubei’s first high-speed rail loop line, playing a significant role in supporting the high-quality development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt and accelerating Hubei’s development as an important strategic pivot for the rise of central China.
Xiangyang East Station
Xiangyang East Station is a major high-speed railway station in Xiangyang, Hubei Province, China, which opened in 2019. It serves as a key hub on the Huhanrong Passenger Dedicated Line, significantly improving regional transportation and connecting the city to the national high-speed rail network.
Xiangjing High-Speed Railway
The Xiangjing High-Speed Railway is a major rail link in China’s Hunan Province, connecting the cities of Xiangtan and Shaoyang. It was constructed to improve regional transportation and economic integration, officially opening to traffic in late 2022. The line forms a crucial part of the Hunan regional high-speed rail network, significantly reducing travel time between the two cities.
Jingmen West Station
Jingmen West Station is a modern high-speed railway station in Hubei Province, China, which opened in 2012. It primarily serves the Hanyi (Hankou–Yichang) intercity railway, significantly improving regional transportation. The station was built to accommodate the growing demand for high-speed rail travel and to support the economic development of the Jingmen area.
Yicheng Station
Yicheng Station is a railway station located in Yicheng, Hubei Province, China, serving the Jiaozuo–Liuzhou railway. It was originally established during the railway’s construction, which began in the 1950s and was completed in the 1970s, to facilitate transport and economic development in the region. Today, it primarily provides passenger and freight services to the local area.
Zhengzhou-Chongqing High-Speed Railway
The Zhengzhou-Chongqing High-Speed Railway is a major transportation artery in central China, officially opening in 2022 after six years of construction. It significantly reduces travel time between the two cities and is renowned for its engineering, as over 90% of its route consists of bridges and tunnels built through the mountainous terrain of the Qinling and Daba ranges.
Shanghai-Chongqing-Chengdu High-Speed Railway
The Shanghai-Chongqing-Chengdu High-Speed Railway is a major transportation artery in China, connecting the eastern economic hub of Shanghai with the key inland cities of Chongqing and Chengdu. Its construction, completed in phases with the final section opening in the late 2010s, was a monumental engineering feat that involved building numerous tunnels and bridges through mountainous terrain. This railway has significantly shortened travel times and boosted economic integration across the Yangtze River Economic Belt.
Eight Vertical and Eight Horizontal
I am unable to identify a specific cultural or historical site known as “Eight Vertical and Eight Horizontal.” This term may refer to a local concept, a translation of a specific place name, or a description of a layout rather than a formally recognized site. To provide an accurate summary, I would need more context or the name in its original language.
Hohhot-Nanning Corridor
The Hohhot-Nanning Corridor is not a single cultural site but a major national development strategy in China. It is an economic belt envisioned to connect northern and southern China, stretching from Hohhot in Inner Mongolia to Nanning in Guangxi. The concept is a modern initiative aimed at boosting regional economic integration and development.