1/5
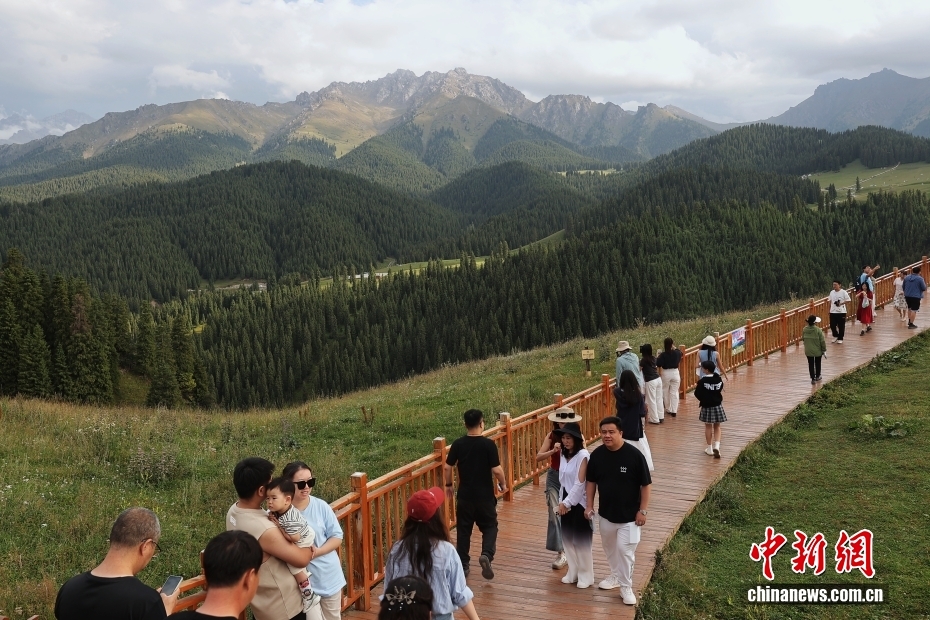
On August 10, the Jiangbulak scenic area in Qitai County, Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang, showcased lush green mountains and breathtaking scenery, attracting numerous tourists. Located at the northern foot of the Tianshan Mountains and the southeastern edge of the Junggar Basin, Jiangbulak means “the source of holy water.”
Jiangbulak scenic area
The Jiangbulak Scenic Area, located in Xinjiang, China, is known for its stunning desert landscapes, unique rock formations, and ancient cultural relics. Historically, it was part of the Silk Road and features remnants of old settlements and petroglyphs, reflecting the region’s rich nomadic heritage. Today, it attracts visitors for its natural beauty and archaeological significance.
Qitai County
Qitai County, located in China’s Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, is known for its rich history as part of the ancient Silk Road and its diverse ethnic culture, including Uygur, Han, and Kazakh communities. The area features historical sites like the ancient city of Jiangjunmiao and scenic landscapes such as the Qitai Desert and grasslands. Its history reflects centuries of trade, cultural exchange, and nomadic traditions.
Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture
Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture is located in northern Xinjiang, China, and is one of the country’s key Hui ethnic autonomous regions. Established in 1954, it has a rich history tied to the Silk Road and is known for its blend of Han Chinese and Hui Muslim cultures. The region is also recognized for its agriculture, trade, and scenic landscapes, including parts of the Tian Shan mountains.
Xinjiang
Xinjiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, is a vast and culturally diverse area in northwest China, known for its rich history as a key part of the ancient Silk Road. It is home to multiple ethnic groups, including the Uyghur, Kazakh, and Han Chinese, and has been a crossroads of trade and culture for centuries. Historically, it was influenced by various empires and is now a region of strategic and economic importance to China, though it has also been a focal point of ethnic tensions and government policies aimed at integration and security.
Tianshan Mountains
The Tianshan Mountains, stretching over 2,500 kilometers across Central Asia, are a majestic mountain range that spans China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Uzbekistan. Known for their stunning glaciers, alpine lakes, and diverse ecosystems, they hold great geographical and cultural significance, historically serving as a key segment of the Silk Road. The Xinjiang portion in China was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2013 for its unique natural beauty and ecological importance.
Junggar Basin
The Junggar Basin is a large sedimentary basin located in northern Xinjiang, China, known for its rich deposits of oil, natural gas, and coal. Historically, it was part of the Silk Road trade routes and home to various nomadic cultures, including the Mongols and Kazakhs. Today, it is a key energy-producing region and features unique desert landscapes like the Gurbantünggüt Desert.