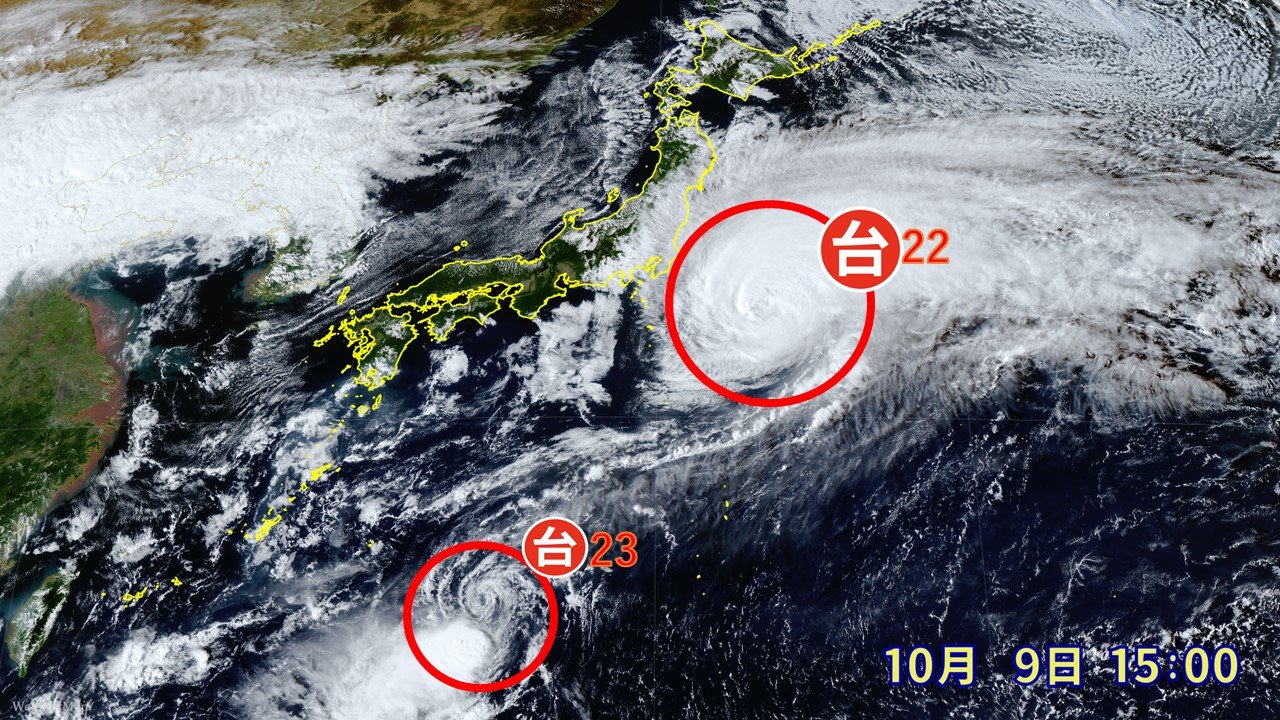
Typhoon No. 23, which formed yesterday, is moving northward over the seas south of Japan.
The forecast area covers southern Kyushu, Shikoku, Kinki, Tokai, Kanto, and the Izu Islands.
A dotted line is drawn through the center of the forecast area, but the typhoon will not necessarily follow this path. There is a 70% probability that the typhoon’s center will enter this area.
Current supercomputer predictions show variations in the timing of when the typhoon will be caught by the westerly winds.
Whether it takes the northernmost path close to the Pacific coast near land or moves significantly further east will greatly change its impact, so please check the latest information.
However, regardless of which path it takes, the Izu Islands, which were affected by Typhoon No. 22, may experience heavy rain and other impacts again. Continued caution is advised for landslides and other hazards.
Izu Islands
The Izu Islands are a volcanic archipelago in Japan stretching south from the Izu Peninsula into the Philippine Sea. Historically, they were used as a place of exile, most notably for the 14th-century Emperor Go-Daigo. Today, the islands are a popular destination known for their hot springs, diverse marine life, and active volcanoes.
Kyushu
Kyushu is the third largest island of Japan, located southwest of the main island of Honshu. Historically, it was the gateway for early cultural exchanges with Korea and China, and it was the site of the first contact with Portuguese traders in the 16th century, which introduced firearms and Christianity to Japan. Today, it is renowned for its active volcanoes, hot springs, and the modern, vibrant city of Fukuoka.
Shikoku
Shikoku is the smallest of Japan’s four main islands, located southwest of the main island of Honshu. It is most famous for the Shikoku Pilgrimage, a 1,200-kilometer circuit of 88 temples associated with the Buddhist monk Kūkai (Kobo Daishi). This ancient pilgrimage route, established centuries ago, remains a deeply spiritual journey that attracts both tourists and ascetic practitioners.
Kinki
“Kinki” is a region in Japan encompassing major cities like Osaka, Kyoto, Kobe, and Nara. Historically, it was the political and cultural heart of classical Japan, serving as the imperial capital for many centuries. Today, it is a vibrant economic center that preserves immense historical significance through its ancient temples, shrines, and cultural traditions.
Tokai
Tokai is a region in central Japan along the Pacific coast, encompassing several major prefectures including Shizuoka and Aichi. Historically, it was a vital part of the important Tokaido travel route that connected the political capital of Kyoto with the city of Edo (modern-day Tokyo). Today, it is a major industrial and economic hub, home to the city of Nagoya and the global headquarters of Toyota.
Kanto
Kanto is a geographical region in Japan encompassing the Greater Tokyo Area and seven prefectures, including Tokyo itself. Historically, it was the center of power for the Tokugawa shogunate during the Edo period (1603-1868), which established its political and economic prominence. Today, it remains Japan’s most populous and economically dominant region.