MANILA – The Speaker of the House of Representatives has reconstituted the Statement of Assets, Liabilities, and Net Worth (SALN) Review and Compliance Committee, pursuant to the provisions of Republic Act 6713 and consistent with his earlier statements regarding revisiting the House’s guidelines on the release of SALNs.
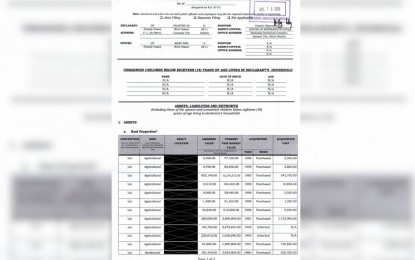
He also released his SALN to the media, following earlier commitments to make his SALN public.
In a memorandum order, a Deputy Speaker was designated as chairperson of the committee, with two representatives serving as vice chairpersons.
The members of the committee include several representatives from various districts and party-list groups.
To provide technical and administrative support, the Secretariat will be composed of senior officials from the Legal Affairs, Legislative Operations, and Administrative Departments, the Office of the Secretary General, the Committee on Rules, and the Records Management Service, along with one representative from the Office of the Speaker.
The reconstitution of the SALN Committee follows the Speaker’s statement that the House will review its rules on the public disclosure of members’ SALNs to ensure transparency and accountability.
In a radio interview, the Speaker shared that House members are generally open to the idea of making their SALNs public.
The Speaker said lawmakers’ SALNs used to be open to public inspection and that Congress should consider returning to that practice.
House of Representatives
The House of Representatives is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, established by the Constitution in 1789. It was designed to represent the people directly, with representation based on population, and is responsible for initiating all revenue bills and impeaching federal officials.
SALN Review and Compliance Committee
The SALN Review and Compliance Committee is a government body responsible for overseeing the submission and verification of Statements of Assets, Liabilities, and Net Worth (SALN) by public officials. It was established to promote transparency and accountability within the government by ensuring that officials declare their wealth accurately and completely. The committee reviews these declarations for potential discrepancies and ensures compliance with anti-corruption and ethical standards laws.
Republic Act 6713
“Republic Act 6713” is not a place or cultural site, but a law in the Philippines. Officially known as the “Code of Conduct and Ethical Standards for Public Officials and Employees,” it was enacted in 1989 to promote high ethical standards in public service. The law establishes duties and responsibilities for government workers, including a mandate to act with integrity and be accountable to the public.
Legal Affairs Department
A Legal Affairs Department is an administrative unit within an organization, such as a corporation or government body, responsible for managing its legal matters. Its history is tied to the increasing complexity of modern law and regulation, which necessitated the creation of specialized internal teams to handle compliance, contracts, and litigation. Rather than a single historic site, these departments are functional entities crucial for the legal and ethical operation of their parent organizations.
Legislative Operations Department
The Legislative Operations Department is a modern administrative body that supports the functioning of a legislative or parliamentary system. It is not a historical or cultural landmark, but a contemporary government office responsible for managing the day-to-day logistical, procedural, and administrative tasks that enable a legislature to operate effectively. Its “history” is tied to the development of the modern bureaucratic state and the increasing complexity of lawmaking.
Administrative Departments
“Administrative Departments” is not a specific place or cultural site, but rather a general term for government offices that manage public services and implement policies. These departments have existed in various forms throughout history, evolving from ancient imperial bureaucracies to the modern civil services found in nations today. They are responsible for the day-to-day governance and administration of a region or country.
Office of the Secretary General
The Office of the Secretary-General is the executive office of the United Nations, headed by the Secretary-General who serves as the chief administrative officer. The role was established with the founding of the UN in 1945 to lead the organization and act as a global diplomat and spokesperson. The office is responsible for overseeing the UN’s operations and agenda, aiming to maintain international peace and security.
Committee on Rules
The Committee on Rules is a powerful standing committee in the United States House of Representatives. Established in 1789, it is often called the “traffic cop” of the House because it determines the rules and procedures for debating and amending most legislation before it reaches the floor. This gatekeeping role gives the committee significant influence over the legislative agenda and the content of bills passed by the House.