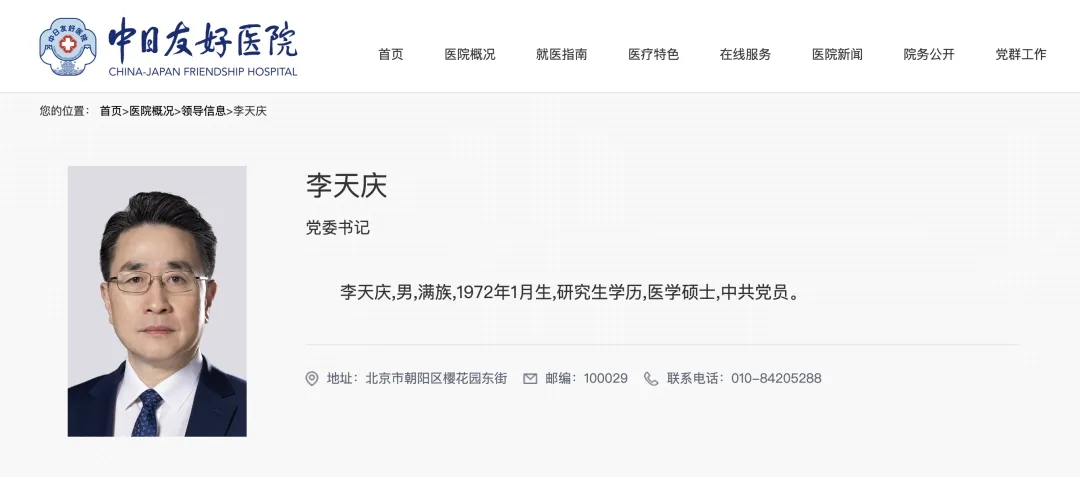
According to the “Leadership Information” section on the official website of the China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Li Tianqing has been appointed as the Party Committee Secretary of the hospital.
Public records show that Li Tianqing was born in January 1972, of Manchu ethnicity, with a postgraduate degree and a Master’s in Medicine.
Li Tianqing worked at the China-Japan Friendship Hospital for many years, holding positions such as Director of Medical Development, Director of the Hospital Office, Director of Security, Director of Infrastructure, Director of the Party Committee Office, and Director of the Party Committee Office concurrently with the Medical Engineering Department.
In July 2019, he became Deputy Party Secretary and Discipline Inspection Commission Secretary of the National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases, as well as Deputy Party Secretary and Discipline Inspection Commission Secretary of Fuwai Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. In December 2021, he was appointed Executive Director of the Henan Cardiovascular Center (Central China Branch of the National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases).
The official website states that the China-Japan Friendship Hospital is a large comprehensive tertiary Grade A hospital directly under the National Health Commission, which opened on October 23, 1984. Previously, the Party Committee Secretary of the hospital was Song Shuli.
China-Japan Friendship Hospital
The China-Japan Friendship Hospital, established in 1984 in Beijing, is a prominent medical institution built as a symbol of cooperation between China and Japan. It was created with Japanese assistance and integrates advanced medical technology and practices from both countries. Today, it serves as a leading hospital in China, specializing in healthcare, research, and medical education.
National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases
The **National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases (NCCD)** is a leading medical institution in China, specializing in the research, prevention, and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Established in the 20th century, it has played a crucial role in advancing cardiac care and public health initiatives in the country. The center combines cutting-edge technology with expert clinical services to improve outcomes for patients with heart-related conditions.
Fuwai Hospital
Fuwai Hospital, officially known as the National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases, is a leading cardiovascular hospital in Beijing, China. Established in 1956, it specializes in cardiovascular disease treatment, research, and prevention, playing a pivotal role in advancing China’s cardiac care. Affiliated with the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, it is recognized for its expertise and high-quality medical services in cardiology and cardiovascular surgery.
Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences
The Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (CAMS), founded in 1956, is China’s leading medical research institution, dedicated to advancing biomedical science, clinical medicine, and public health. It collaborates closely with Peking Union Medical College (PUMC) and has played a key role in major health initiatives, including infectious disease control and medical innovation. Recognized for its contributions to global health, CAMS continues to drive research and education in China’s healthcare system.
Henan Cardiovascular Center
The Henan Cardiovascular Center is a specialized medical institution in Henan Province, China, dedicated to the diagnosis, treatment, and research of cardiovascular diseases. Established to address the growing need for advanced cardiac care, it plays a key role in regional healthcare, offering modern facilities and expertise in heart-related conditions. While its exact founding date is unclear, it reflects China’s broader efforts to improve specialized medical services in recent decades.
Central China Branch of the National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases
The **Central China Branch of the National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases** is a specialized medical institution in China focused on cardiovascular disease treatment, research, and prevention. Established to improve regional healthcare access, it serves as a key hub for advanced cardiac care in Central China, leveraging expertise from the national center. Its history reflects China’s efforts to expand high-quality medical resources and reduce disparities in cardiovascular health outcomes.
National Health Commission
The National Health Commission (NHC) of China is a government agency responsible for national health policies, public health management, and healthcare reform. Established in 2018, it replaced the former National Health and Family Planning Commission, reflecting a greater focus on public health and medical services. The NHC plays a key role in overseeing disease prevention, healthcare access, and major health initiatives, such as responses to epidemics like COVID-19.